arduino – MPU6050 新手学习笔记
1.MPU6050是什么?
MPU6050是一个6轴运动处理组件,包含了3轴加速度 和3轴陀螺仪。
2.加速度传感器是干嘛用的?
这个要结合图片来说明,大家可以看这里:
http://download.csdn.net/download/feixiangtiakongn/4545536
总而言这,加速度传感器,其实是力传感器。用来检查上下左右前后哪几个面都受了多少力(包括重力)
3.陀螺仪是干嘛用的?
简而言之,陀螺仪就是角速度检测仪。比如,一块板,以X轴为轴心,在一秒钟的时间转到了90度,那么它在X轴上的角速度就是 90度/秒 (DPS, 角速度单位,Degree Per Second的缩写°/S ,体现了转动的快慢)
4.MPU6050分辨率是多少?
3轴加速度 和3轴陀螺仪分别用了3个16位的ADC, 也就是说,加速度有3个16位ADC,其中每个轴使用了一个。也是说,每个轴输出的数据,是2^16 也就是 -32768 —- +32768。陀螺仪也是一样。
5. 单位换算
上面说的-32768 — +32768 ,那么这个数字到底代表了什么呢?比如陀螺仪 32768 到底是指角速度达到多少度/秒 ?
这个其实是根据MPU6050设置的量程来决定的,量程不一样,32768代表的值就不一样。
MPU6050的量程设置,在 MPU6050::initialize() (MPU6050.cpp库)初始化函数中进行了设置:
setFullScaleGyroRange(MPU6050_GYRO_FS_250);
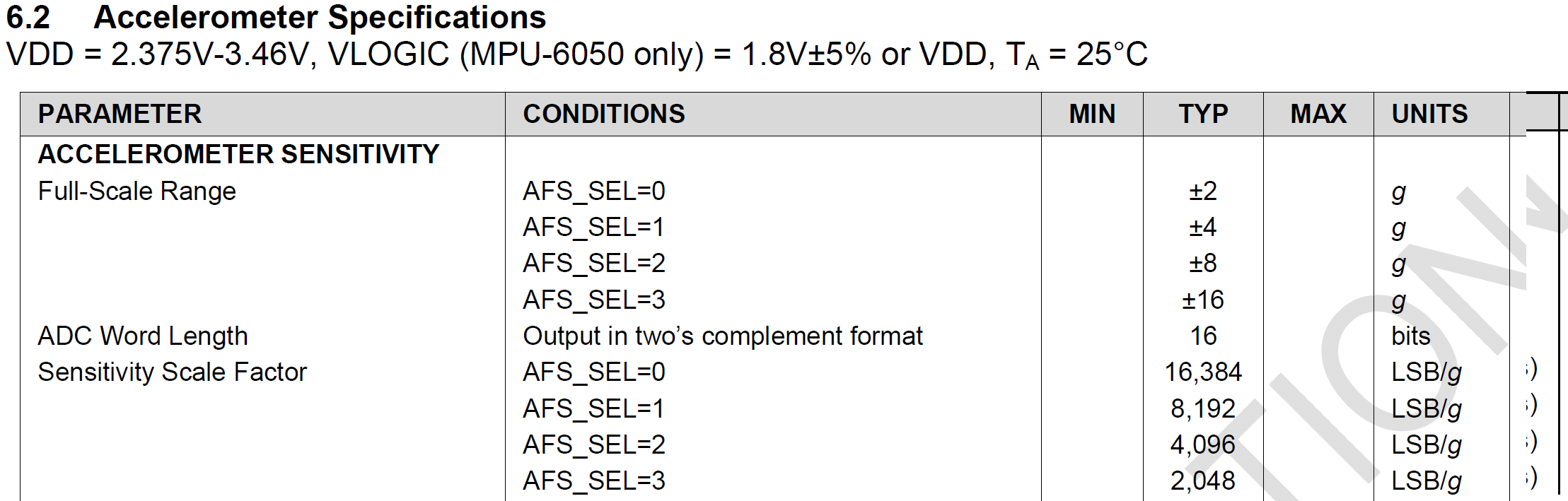
setFullScaleAccelRange(MPU6050_ACCEL_FS_2);
分别设置为,250度/秒 , 2g
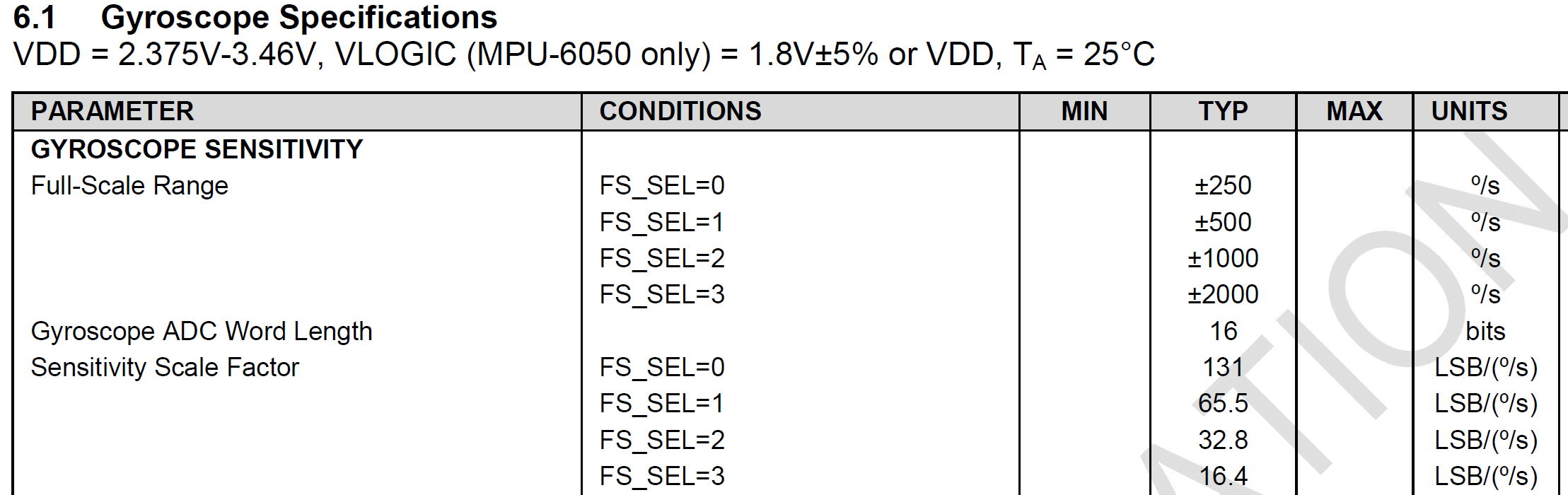
按陀螺仪来说,MPU6050 有四个量程可选:
±250,±500,±1000,±2000 度/s
比方说,设置了是 ±250 , 那么-32768 —- +32768 就代表了 -250 —- +250 。此时它的LSB(拉傻B,最低有效位) 是 131 LSB/(度/s)
MPU 6050 读角度与单位换算
参考数据手册:PS-MPU-6000A
使用带有DMP的最新库函数(https://github.com/jrowberg/i2cdevlib),程序模板采用MPU6050_DMP6例程。
角度:
DMP库函数的dmpGetYawPitchRoll,可以得到pitch(俯仰),yaw(偏航),roll(滚转)角度。
角速度:
void getRotation(int16_t* x, int16_t* y, int16_t* z);
int16_t getRotationX();
int16_t getRotationY();
int16_t getRotationZ();
16位,配置时四个量程可选:±250,±500,±1000,±2000 度/s。
在dmp的例程中初始化:setFullScaleGyroRange(MPU6050_GYRO_FS_2000);
说明是选用最高量程±2000º/s,则换算系数=2^16/4000=16.4 LSB/(度/s)

博主知道怎样调节mpu6050的采样频率吗
谢谢分享!!!
这个传感器获取数据容易,处理数据就难了啊!加油!
说的是啊。数据得到了,进行数据删选,过滤,分析,进行计算,这一系列的事情才是最头疼的。
对呢。在用Arduino进行数据获取时,有很方便的库和IIC借口进行获取,就是波特率的选择,以及数据获取到之后的处理,让我真心觉得不好弄。
还有,在进行数据获取时,波特率用9600在做运动检测时够用吗?请赐教!
我也没有具体测试,如果以后测试有心得了会告诉你。
好的,期待!